As the demand for clean green hydrogen grows, electrolyser demand will grow in tandem. This article details which electrolyser components will seize market value based on adoption of different electrolyser technology solutions.
Together, these trends are supporting the build-out of global green hydrogen infrastructure.
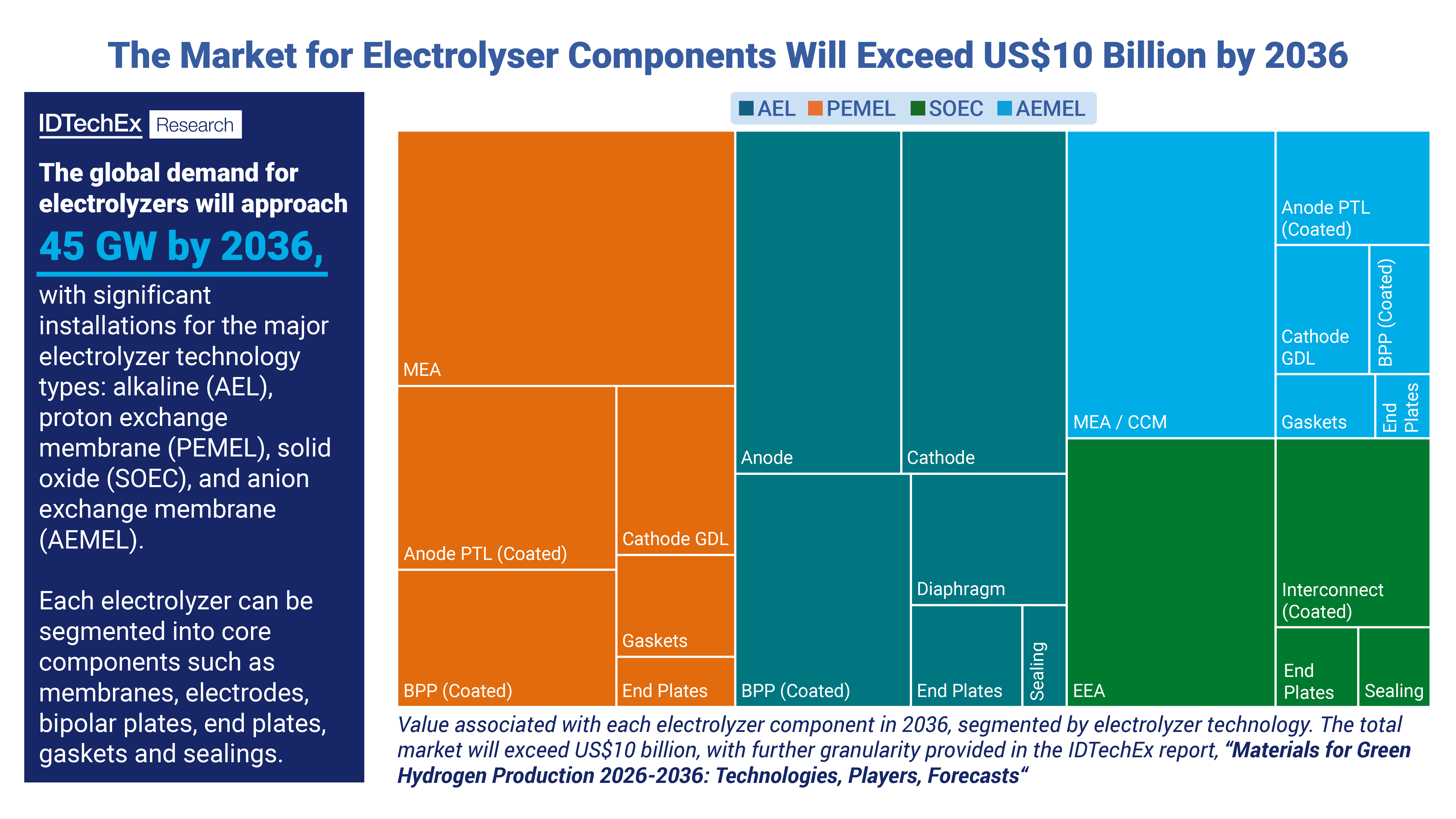
An overview of the component market for electrolysers, set to exceed US$10 billion by 2036. Source: IDTechEx, “Materials for Green Hydrogen Production 2026-2036: Technologies, Players, Forecasts”.
Which Electrolyzer Technology Will Dominate?
The global demand for electrolysers will approach 45 GW by 2036, with significant installations for the major electrolyzer technology types: alkaline (AEL), proton exchange membrane (PEM), solid oxide (SOEC), and anion exchange membrane (AEMEL). IDTechEx have forecast the global adoption, taking into account announced projects, electrolyser manufacturing capacities and global policies, while also considering the current challenges being faced by the hydrogen sector globally (e.g. slower project development, US policy uncertainty).
AEL is expected to be the dominant technology, with PEMEL being the second largest. Between the two leading technologies, AEL and PEMEL will account for almost 80% of the market by the end of the decade. AEMEL and SOEC installations are predicted to be relatively small in comparison due to them being more novel technologies, with manufacturing still scaling up.
The Value of Electrolyser Components is Not Uniform
Each electrolyser can be broken down into constituent components with varying share of the value associated with each component. Taking the example of an AEL stack, IDTechEx provide detailed analysis of components such as bipolar plates, anode, cathode, diaphragm, end plates and sealing, with this repeated for PEMEL, SOEC and AEMEL. In general, the membrane electrode assembly (MEA), consisting of the electrodes and the membrane/electrolyte, has the largest share of the stack cost. Other components like the bipolar plates and coatings also contribute significantly.
The cost of components and combined stack differs by electrolyser technology. Despite AEL being the leader by installations, PEMEL components are likely to seize a larger portion of the total market value due to the higher cost associated with individual components. A notable example here is the use of platinum group metal catalysts, with significant focus of R&D on reducing the cost of the catalyst in both PEM electrolyzers and fuel cells. The major trends seen are the optimisation of catalyst application to reduce wastage, or the development of alternative materials with a lower price point.



